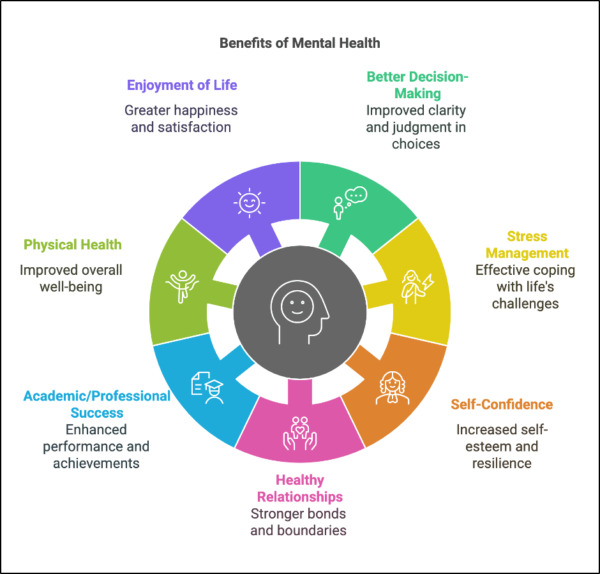
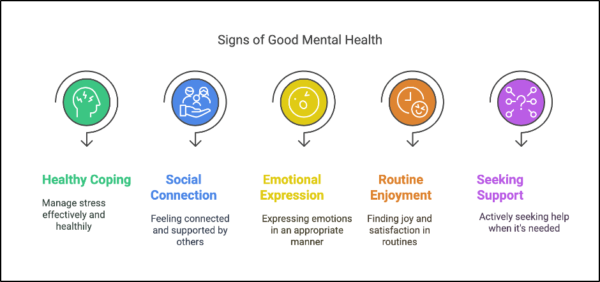
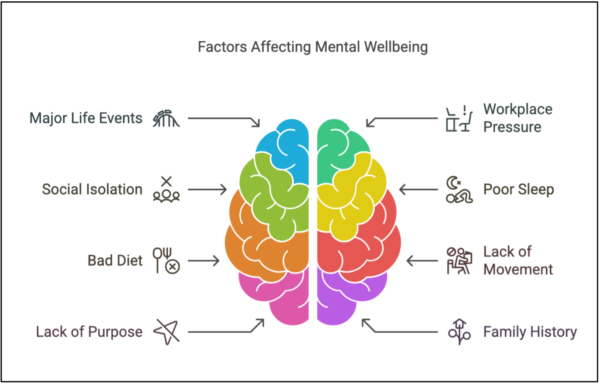
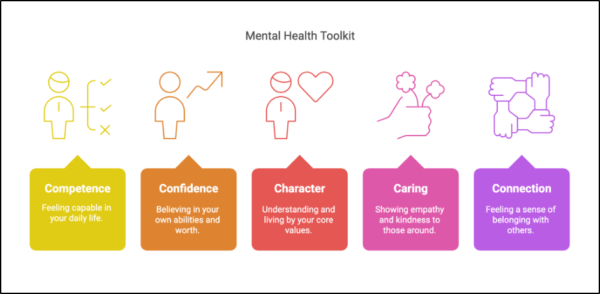
At Mind Medicine Australia, we are dedicated to transforming the treatment of mental illness by expanding access to evidence-based psychedelic-assisted therapies. As a leading charity in the field, we support the development and clinical implementation of innovative therapies involving psilocybin and MDMA. These treatments, supported by international research, offer renewed hope to Australians experiencing persistent mental health challenges.

Why We Need New Solutions
In Australia today, one in four people live with a mental illness, and current treatments are often insufficient. We understand the frustration and despair that can arise when conventional options don’t work. Research shows that over 50% of individuals do not respond to existing therapies such as SSRIs or talk therapy alone. This underscores the urgent need for innovative solutions that address the root causes of suffering more effectively and compassionately.
What Are Psychedelic-Assisted Therapies?
Psychedelic-assisted psychotherapies involve the use of psychedelic compounds, such as psilocybin and MDMA, combined with psychotherapy. These treatments follow a three-phase model: preparation, experience, and integration. These sessions are held in safe, therapeutic environments under the supervision of trained professionals. Patients are carefully screened and supported throughout the process to ensure safety and maximise outcomes.

Image: Increased communication between brain networks (based on fMRI scans): Brain imaging comparison before (left) and after (right) psilocybin treatment. Source: Beckley Foundation, United Kingdom. Based on clinical trials at Imperial College, London
Clinical trials at leading institutions—including Johns Hopkins University and Imperial College London—have consistently shown that these therapies can lead to remission in patients with treatment-resistant conditions, such as depression and PTSD. In fact, international studies have found that psilocybin and MDMA-assisted therapy has resulted in 60-80% remission rates after 2-3 medicinal treatments in combination with a short course of psychotherapy for the treatment of PTSD and depression. They are often rated by patients as among the most meaningful experiences of their lives.
How Mind Medicine Australia Made History
In 2023, following advocacy efforts by Mind Medicine Australia, the Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) approved the rescheduling of psilocybin and MDMA for controlled clinical use. This landmark decision makes Australia the first country to formally allow treatments in clinical environments.
Since January 2024, 100+ patients have been treated in clinics across Australia as part of the Therapeutic Goods Administration’s (TGA) Authorised Prescriber (AP) program with medicines and training supplied through Mind Medicine Australia.
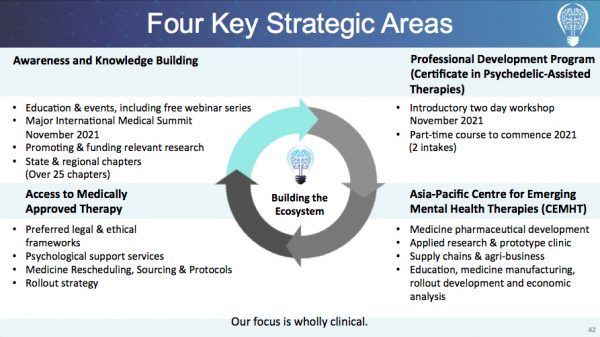
This milestone builds on six years of sector leadership, during which we’ve trained over 500 clinicians through our globally recognised Certificate in Psychedelic-Assisted Therapies (CPAT)™ program, secured $15 million in federal research funding, supported the launch of clinics nationwide, and funded groundbreaking trials for conditions like OCD and PTSD. With over 3,500+ individuals educated through workshops and courses and public outreach reaching hundreds of thousands, we’re not just supporting individual healing—we’re transforming mental healthcare in Australia and beyond.
World-Leading Training

We offer professional education through our Certificate in Psychedelic-Assisted Therapies (CPAT)™, training clinicians in best practices. This hybrid program (online + face-to-face) is for registered healthcare professionals—psychiatrists, psychologists, psychotherapists, counsellors, and more—who want to deliver psychedelic-assisted therapy using psilocybin and MDMA in clinical settings. The training is delivered by a world-class faculty made up of global leaders in the field including Dr Gabor Maté CM (Canada), Dr Bessel van der Kolk (USA), Dr Rick Doblin (USA), and many more. We’ve received outstanding feedback for the program:
“One of the things I’ve been doing a lot in the last year is teaching on the Mind Medicine Australia training course, which I think is the best course in the world for educating people about how to use psychedelics and how to develop, through that, in Australia, several hundred people who have the competencies and knowledge to potentially be therapists for this kind of treatment.” – Professor David Nutt (UK), ABC News
How You Can Help
Our vision includes establishing more clinical programs, making therapies accessible, and ensuring long-term safety and effectiveness through continued research and community engagement. We believe these treatments have the power to revolutionise mental health care in Australia, but only when delivered safely, ethically, and responsibly. We are committed to supporting access to treatments that can truly make a difference, which is why we have created our Patient Support Fund (PSF).
The Patient Support Fund (PSF) subsidises treatment costs for Psychedelic-Assisted Therapies in Australia to support equitable access. The total amount committed so far is over $100,000 AUD. We have also received further funding requests for 2025. Please help us to make psychedelic-assisted therapies accessible for all Australians who need them by donating today.
Together, with continued research, compassionate care, and community support, we can bring these life-changing therapies to those who need them most—offering not just treatment, but hope for healing and brighter futures.
Disclaimer: This post is provided by Mind Medicine Australia for educational purposes only. It does not constitute medical advice. Psychedelic-assisted therapies are available only through approved clinicians in accordance with the Therapeutic Goods Administration guidelines. Always consult with a qualified health professional regarding your treatment options.